Five European organizations from Serbia, Germany and France and three non-European institutions from New Zealand, Australia and Thailand will unite around the MEDLEM Project to make significant breakthrough in research against leukemia.
The main idea behind the MEDLEM Project is to establish which chemotherapy is to be assigned to each individual patient in order to improve the chances for cure, decrease side effects and ensure that the total toxicity is below an allowable limit.
Challenges in leukemia treatment
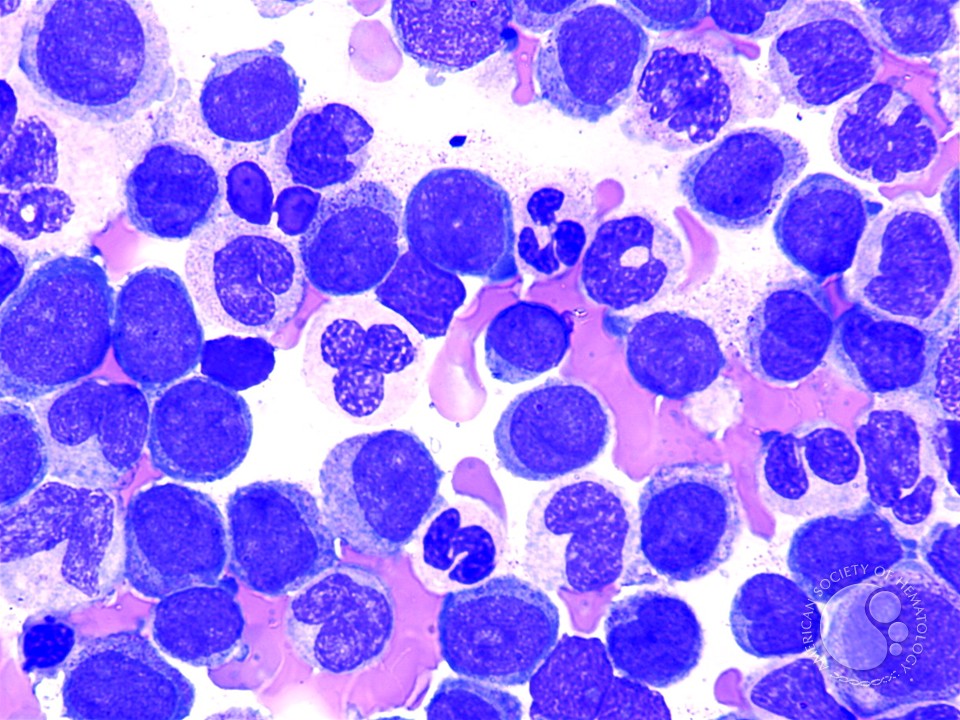
Leukemia is a group of cancers that starts in blood-forming tissue and causes large numbers of abnormal blood cells to be produced and enter the bloodstream. Worldwide, over 250,000 people are diagnosed  with leukemia each year, accounting for 2.5% of all cancers. An estimated 75,000 new patients of leukemia will be diagnosed in Europe every year (about 40,000 in USA). All age groups can be affected; leukemia is the most common pediatric tumor (35% of cancers in children aged 0–14 years).
with leukemia each year, accounting for 2.5% of all cancers. An estimated 75,000 new patients of leukemia will be diagnosed in Europe every year (about 40,000 in USA). All age groups can be affected; leukemia is the most common pediatric tumor (35% of cancers in children aged 0–14 years).
The breakthroughs in diagnostics, therapy and improvements to therapy protocols have all led to long-term curing, with an overall five-year survival rate of almost 80% in children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL). There is an utmost need for new treatments and new high-tech devices which can help in customized therapy of leukemia. The MEDLEM Project addresses this challenge.
The Medlem project goals
Implementation of the MEDLEM Project will help in both detection of high risk patients, especially children, and general improvement of the human condition during invasive treatment, what chemotherapy definitely is.
Its overall goal is to increase five and ten-year survival rates of patients with leukemia, in Europe and globally.
 The MEDLEM Project involves three areas of research (Biomechanics, Medicine/Pharmacy and Electronics) in a unique fusion of knowledge with purpose to improve leukemia treatments. Microfluidic devices will be designed and optimized, reaching breakthroughs in modeling, drug administration and improvements in therapy protocols. Furthermore, microfluidic devices which will manage drug delivery, will be low cost, light weight and shock resistant. Long-term, high quality research providing improvement and important progress in leukemia treatments will be built up.
The MEDLEM Project involves three areas of research (Biomechanics, Medicine/Pharmacy and Electronics) in a unique fusion of knowledge with purpose to improve leukemia treatments. Microfluidic devices will be designed and optimized, reaching breakthroughs in modeling, drug administration and improvements in therapy protocols. Furthermore, microfluidic devices which will manage drug delivery, will be low cost, light weight and shock resistant. Long-term, high quality research providing improvement and important progress in leukemia treatments will be built up.
A new community of researchers
Intensive scientific exchange will be performed which will enable to establish a new, common, worldwide research area. Scientific cooperation between Europe and third countries should contribute to global approaches and solutions to societal challenge. Knowledge reached in the field will increase awareness for innovative solutions for leukemia treatment providing significant benefits for European and worldwide society.
Hadrien Vielle

Author
Auteur
Hadrien is an engineer and was trained in biology, physics and bio-engineering at the École Polytechnique féminine in Paris.
More about the Long Long Life team
Hadrien est aujourd’hui ingénieur polyvalent après une formation en biologie, physique et bio-ingénierie à l’École Polytechnique féminine.
En savoir plus sur l’équipe de Long Long Life